Simple Syntax
CASE selector when expr1 then value1 when expr2 then value2 ... when exprN then valueN else value 3
The else clause is optional. The alternative is selected based on the value of the selector.
Searched Syntax
This one has no selector. The alternative expressions are evaluated and if true that choice is used.
CASE when expr1 then value1 when expr2 then value2 ... when exprN then valueN else value 3
Simple Example
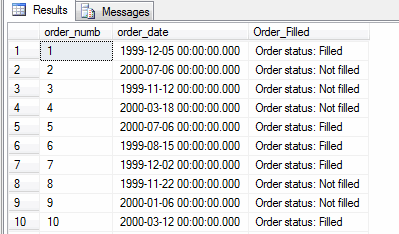
Here is an example of this syntax. It expands the order_filled yes/no field.
use bookstore; select order_numb, order_date, case order_filled
when 'Yes' then 'Order status: Filled' when 'No' then 'Order status: Not filled' else 'Errorneous order status detected' end 'Order_Filled'from orders;
Simple Results
Searched CASE example
This example below shows who referred a customer. If the customer was not referred by another customer we print "self". In this case we cannot use a selector since it might evaluate to a null which leads to no defined choice. Instead, this example uses a searched case which separately evaluates each condition. You have to do it this way if the field you might use for a selector can contain nulls.
use bookstore;
select c.customer_first_name
, c.customer_last_name
, case when c.referred_by is null then 'Self' else r.customer_last_name
end as 'Referred By'from customers c left join customers r on c.referred_by = r.customer_numb;
Searched CASE reuslts
Conclusion
The CASE expression can be very helpful when you need to choose between several alternatives. I am sure you will find it useful. Note there is another similar keyword - DECODE - used in Oracle.

